Terpenes and Their Effects on the Body: An In-Depth Exploration of the Five Most Prominent Terpenes
Introduction
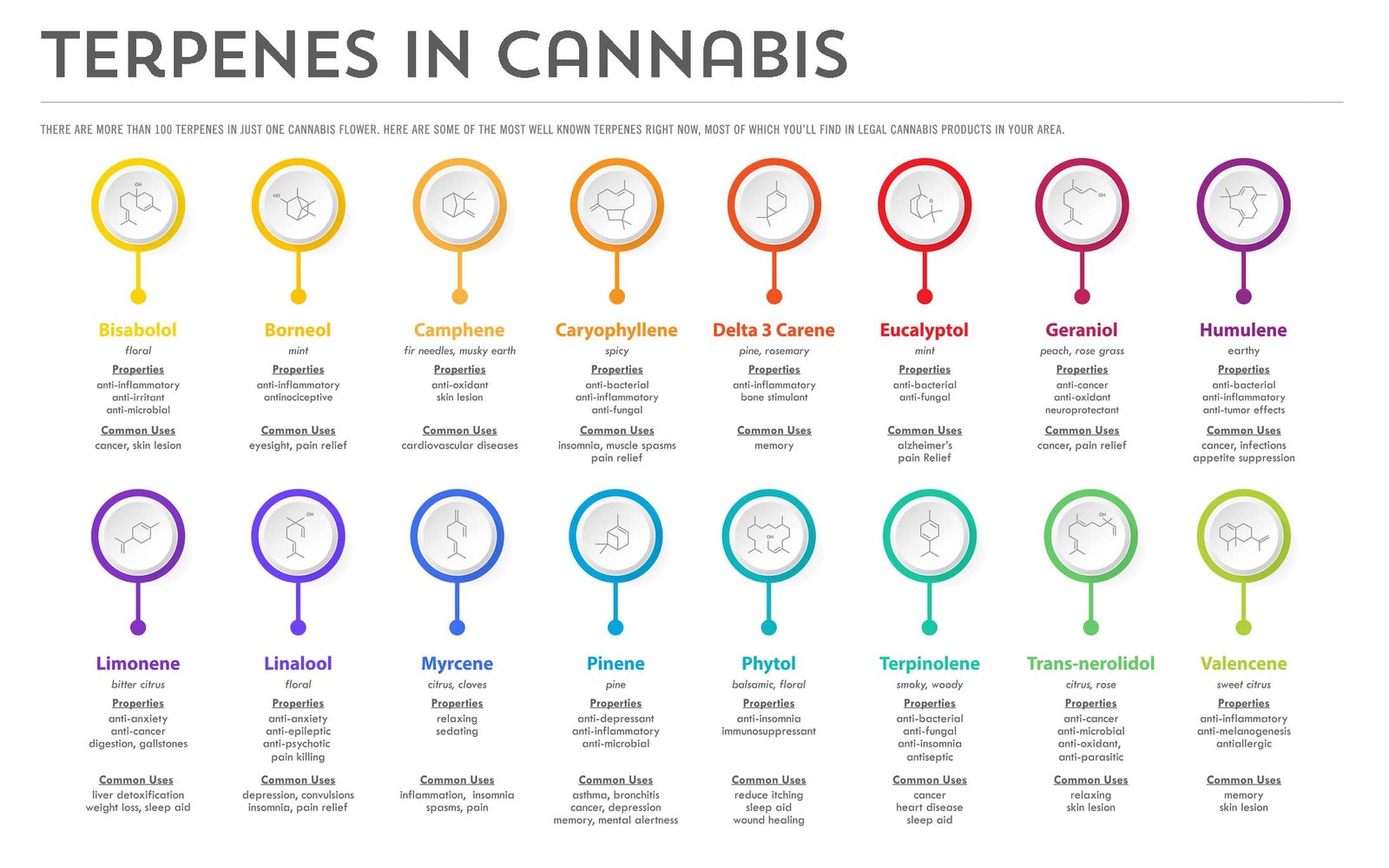
Terpenes are organic compounds found in a variety of plants, most notably in cannabis, where they contribute to its distinct aroma and flavour. Beyond their role in plants, terpenes have become a focus of scientific research due to their therapeutic potential for human health. These compounds not only play a crucial role in the plant’s defence mechanisms against herbivores and pathogens, but they also interact with the human body, influencing physiological and psychological processes. With increasing interest in natural medicines and cannabis research, terpenes have gained recognition for their health-promoting properties, particularly their ability to modulate mood, reduce inflammation, and support immune function.
This article explores the five most prominent terpenes—limonene, myrcene, pinene, linalool, and beta-caryophyllene—each of which exhibits unique medicinal properties and exerts specific effects on the human body. We will delve into their interactions with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), how they complement cannabinoids like THC and CBD in the “entourage effect,” and their potential for therapeutic applications in modern medicine. This comprehensive examination will also cover how different extraction methods influence terpene efficacy, their effects on mental health, and the evolving role of synthetic terpenes in medical research.
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are volatile organic hydrocarbons produced by a wide range of plants and some animals. In nature, they serve a defensive role, protecting plants from herbivores, insects, and environmental stressors. They are responsible for the distinct scents of many plants, including pine trees, citrus fruits, and flowers, and have been used for centuries in traditional medicine, aromatherapy, and perfumes.
In the context of cannabis, terpenes contribute not only to the plant’s smell and flavor but also to its therapeutic effects. Terpenes can modulate the psychoactive effects of cannabinoids and interact with various receptors in the human body, influencing mood, inflammation, pain perception, and even memory. They are synthesized from isoprene units in the plants and can be classified into monoterpenes (two isoprene units), sesquiterpenes (three isoprene units), and diterpenes (four isoprene units).
The potential benefits of terpenes extend beyond cannabis, as they have been identified in many plants, including herbs, spices, and fruits, and are used extensively in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
Terpenes and Human Health
Terpenes interact with the body’s physiological systems, notably the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which plays a central role in maintaining homeostasis, affecting processes such as pain, mood, appetite, and immune response. Some terpenes directly bind to receptors in the ECS, while others indirectly modulate cannabinoid signaling pathways. Furthermore, terpenes exhibit diverse biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, neuroprotective, and anxiolytic properties, making them valuable therapeutic agents.
The Five Most Prominent Terpenes and Their Effects
1. Limonene
Medicinal Properties and Benefits for the Body
Limonene is a citrus-scented monoterpene predominantly found in citrus fruits such as lemons, limes, and oranges. It has been studied extensively for its anti-anxiety, antidepressant, and anti-inflammatory effects. Limonene is also known for its antioxidant properties and its ability to modulate immune responses.
Interaction with the Endocannabinoid System
Limonene does not directly bind to cannabinoid receptors but influences the ECS by altering serotonin and dopamine neurotransmitter systems, contributing to its mood-enhancing and anxiolytic effects. It enhances the absorption of other terpenes and cannabinoids, increasing their bioavailability and contributing to the entourage effect.
Interaction with Cannabinoids and the Entourage Effect
When combined with cannabinoids like THC and CBD, limonene enhances their therapeutic effects. Its ability to increase cell membrane permeability allows cannabinoids to be more effectively absorbed, potentially amplifying their effects on the ECS, particularly in reducing anxiety and depression.
Mental Health Applications
Limonene’s impact on mental health has been observed in studies where it exhibits anxiolytic and antidepressant properties by modulating serotonin levels. It has been used in aromatherapy for stress reduction, showing efficacy in reducing anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders.
Popular Cannabis Strains Containing Limonene
Strains high in limonene include Super Lemon Haze, Durban Poison, and Jack Herer. Users often report feelings of euphoria, elevated mood, and stress relief when consuming strains rich in limonene.
Biochemical Mechanisms
Limonene activates TRP channels and influences cAMP signaling pathways, which can affect inflammatory responses and mood regulation. It also plays a role in the upregulation of enzymes involved in detoxification, providing additional benefits in cancer prevention research.
2. Myrcene
Medicinal Properties and Benefits for the Body
Myrcene is one of the most abundant terpenes in cannabis and is also found in high concentrations in hops, mangoes, and lemongrass. It is known for its sedative, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory effects. Myrcene enhances the permeability of cell membranes, facilitating the uptake of cannabinoids.
Interaction with the Endocannabinoid System
Myrcene modulates the ECS by increasing the affinity of CB1 receptors for endogenous cannabinoids and phytocannabinoids like THC. This potentiates the psychoactive and analgesic effects of THC, which can help in the management of pain and sleep disorders.
Interaction with Cannabinoids and the Entourage Effect
Myrcene enhances the sedative and relaxing effects of cannabinoids. It is believed to be a key component of the entourage effect, synergizing with THC and CBD to produce a more profound sedative effect, beneficial for insomnia, chronic pain, and anxiety.
Mental Health Applications
Due to its sedative properties, myrcene is often recommended for treating anxiety and insomnia. Its relaxing effects help calm the nervous system, making it an excellent choice for patients with stress-related disorders and sleep disturbances.
Popular Cannabis Strains Containing Myrcene
Strains rich in myrcene include Granddaddy Purple, Blue Dream, and OG Kush. Users report profound relaxation, pain relief, and a calming sensation when using strains with high myrcene content.
Biochemical Mechanisms
Myrcene acts on GABAergic pathways, contributing to its sedative effects. It also interacts with transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, which play a role in the perception of pain and inflammation, making it an important terpene for pain relief and neuroprotection.
3. Pinene
Medicinal Properties and Benefits for the Body
Pinene is a bicyclic monoterpene found in coniferous trees like pine and fir, as well as in rosemary and basil. It is known for its anti-inflammatory, bronchodilator, and memory-enhancing effects. It can also act as an antimicrobial agent, showing promise in combating respiratory infections.
Interaction with the Endocannabinoid System
Pinene has an indirect effect on the ECS by inhibiting the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in memory and cognitive function. This inhibition may counteract memory impairment caused by THC, providing a cognitive-balancing effect when consumed alongside THC-rich strains.
Interaction with Cannabinoids and the Entourage Effect
Pinene’s interaction with THC can mitigate some of the negative cognitive side effects, such as short-term memory loss. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties complement the analgesic effects of CBD, making it beneficial for conditions like arthritis and chronic pain.
Mental Health Applications
Pinene’s influence on acetylcholine levels makes it an important terpene for cognitive enhancement and memory preservation. It may also have anxiolytic properties, though more research is needed to fully understand its effects on mental health.
Popular Cannabis Strains Containing Pinene
Strains high in pinene include Jack Herer, Strawberry Cough, and Chemdawg. Users often report feelings of clarity, focus, and alertness when consuming these strains.
Biochemical Mechanisms
Pinene interacts with cholinergic systems, enhancing acetylcholine transmission and improving cognitive function. It also acts on inflammatory pathways, such as the NF-kB pathway, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, which may offer protective effects against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
4. Linalool
Medicinal Properties and Benefits for the Body
Linalool is a floral-scented monoterpene found in lavender, coriander, and rosewood. It is well-known for its sedative, anti-anxiety, and anticonvulsant properties. Linalool also has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, making it a versatile therapeutic agent.
Interaction with the Endocannabinoid System
Linalool interacts with the ECS by modulating GABAergic neurotransmission, enhancing the relaxing and sedative effects of CBD. It also influences serotonin receptors, contributing to its mood-stabilizing effects.
Interaction with Cannabinoids and the Entourage Effect
Linalool’s synergy with cannabinoids enhances their sedative and anxiolytic effects. Combined with CBD, linalool can be particularly effective for patients with anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. Its anticonvulsant properties are also of interest for treating epilepsy.
Mental Health Applications
Linalool has been shown to have potent anxiolytic and antidepressant effects. It has been used in aromatherapy to reduce anxiety and promote sleep, particularly in patients with insomnia or PTSD.
Popular Cannabis Strains Containing Linalool
Strains rich in linalool include Lavender, LA Confidential, and Amnesia Haze. Users typically report calming effects, relief from anxiety, and improved sleep quality.
Biochemical Mechanisms
Linalool enhances GABA receptor activity, contributing to its calming and sedative effects. It also modulates 5-HT1A receptors, impacting serotonin transmission and influencing mood regulation, making it a valuable terpene for mental health applications.
5. Beta-Caryophyllene
Medicinal Properties and Benefits for the Body
Beta-caryophyllene is a spicy, peppery sesquiterpene found in black pepper, cloves, and cinnamon. It is unique among terpenes because it directly binds to CB2 receptors in the ECS, exhibiting anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anti-anxiety properties. It is also recognized for its potential in treating inflammatory diseases.
Interaction with the Endocannabinoid System
Beta-caryophyllene interacts with the ECS by selectively binding to CB2 receptors, which are primarily located in the immune system. This binding action helps reduce inflammation, modulate immune responses, and provide relief from chronic pain.
Interaction with Cannabinoids and the Entourage Effect
Beta-caryophyllene’s direct action on CB2 receptors enhances the effects of CBD, particularly in terms of pain relief and anti-inflammatory responses. It also works synergistically with THC, enhancing its therapeutic potential without intensifying its psychoactive effects.
Mental Health Applications
Beta-caryophyllene’s influence on CB2 receptors contributes to its anxiolytic and antidepressant effects. It has shown promise in treating anxiety disorders, depression, and even conditions related to neuroinflammation, such as multiple sclerosis.
Popular Cannabis Strains Containing Beta-Caryophyllene
Strains high in beta-caryophyllene include Girl Scout Cookies, Sour Diesel, and Chemdawg. Users often report relief from chronic pain, inflammation, and stress, with little to no psychoactive effects.
Biochemical Mechanisms
Beta-caryophyllene’s ability to bind to CB2 receptors distinguishes it from other terpenes. Its activation of these receptors modulates immune responses and reduces inflammatory cytokines, offering therapeutic potential for a wide range of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders.
Terpene Extraction Methods and Their Impact on Potency and Efficacy
Different methods of extracting terpenes, such as steam distillation and CO2 extraction, influence their potency, efficacy, and therapeutic value. Steam distillation is a common method that relies on heat and water vapor to extract essential oils from plant material. While effective, the high temperatures can degrade some of the more delicate terpenes. CO2 extraction, on the other hand, uses pressurized carbon dioxide to extract terpenes at lower temperatures, preserving more of their original potency and structure.
The choice of extraction method can impact the entourage effect, as some methods may selectively preserve or degrade certain terpenes, altering their synergy with cannabinoids and other compounds.
Terpenes and Mental Health
Terpenes have shown significant potential in the treatment of mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and stress. Aromatherapy utilizing terpenes like linalool and limonene has been used for centuries to promote relaxation and mood enhancement. Recent studies suggest that terpenes can influence neurotransmitter systems, modulating serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, which are critical for mental health.
Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of terpene-rich essential oils in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. Moreover, terpenes combined with cannabinoids have shown promise in treating PTSD and sleep disorders.
Synthetic Terpenes in Medical Research
The development of synthetic terpenes offers exciting opportunities for medical research. These lab-created compounds can mimic the properties of natural terpenes while offering greater consistency and purity. Synthetic terpenes are being studied for their potential to treat neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and chronic pain. By isolating specific properties, researchers can target individual receptors more effectively, which may lead to the development of tailored therapies with fewer side effects.
One advantage of synthetic terpenes is their stability, which allows for precise dosing and the creation of standardized medications. This could be particularly valuable in personalized medicine, where therapies are customized to an individual’s specific terpene and cannabinoid profile.
Terpene-Phytochemical Interactions
Terpenes interact with other phytochemicals, such as flavonoids, to create synergistic effects that can enhance their therapeutic potential. Flavonoids, which are also found in cannabis and many fruits and vegetables, have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Together with terpenes, they can amplify effects such as pain relief, mood enhancement, and neuroprotection.
This synergy between terpenes and flavonoids is an emerging area of research, particularly in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. The combined effects of these compounds could potentially lead to more effective treatments with fewer side effects than traditional pharmaceuticals.
Terpenes in Personalized Medicine
In clinical settings, terpenes are increasingly being explored as part of personalized medicine. By analyzing an individual’s genetic makeup and endocannabinoid profile, healthcare providers can tailor terpene and cannabinoid treatments to meet specific needs. For example, a patient with chronic pain might benefit from a combination of myrcene, CBD, and beta-caryophyllene, while someone with anxiety might respond better to linalool and limonene.
The ability to customize terpene profiles for individual patients could revolutionize the treatment of a wide range of conditions, from anxiety and chronic pain to autoimmune diseases and cancer.
Terpenes in Neuroprotection
Terpenes have shown significant promise in the field of neuroprotection, particularly in the treatment of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders. Terpenes like pinene, linalool, and beta-caryophyllene have been studied for their ability to reduce neuroinflammation, protect neurons from oxidative stress, and promote neurogenesis.
In Alzheimer’s disease, for example, terpenes like pinene have been shown to enhance memory and cognitive function by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme responsible for breaking down acetylcholine in the brain. Similarly, linalool has demonstrated anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that could help protect neurons from degeneration.
Conclusion
Terpenes represent a fascinating area of study with broad implications for human health. Their ability to interact with the endocannabinoid system, modulate inflammation, influence mood, and protect neurons positions them as valuable therapeutic agents. While much progress has been made in understanding the potential benefits of terpenes, there remain gaps in research, particularly in terms of clinical applications and personalized medicine.
Future research will likely focus on the synergy between terpenes, cannabinoids, and other phytochemicals, as well as the development of synthetic terpenes for targeted therapies. As the medical community continues to explore the therapeutic potential of terpenes, they may play a key role in the development of new treatments for mental health disorders, chronic pain, neurodegenerative diseases, and beyond. The promise of personalized medicine, where therapies are tailored to an individual’s unique biological profile, further underscores the importance of continuing research into this remarkable class of compounds.